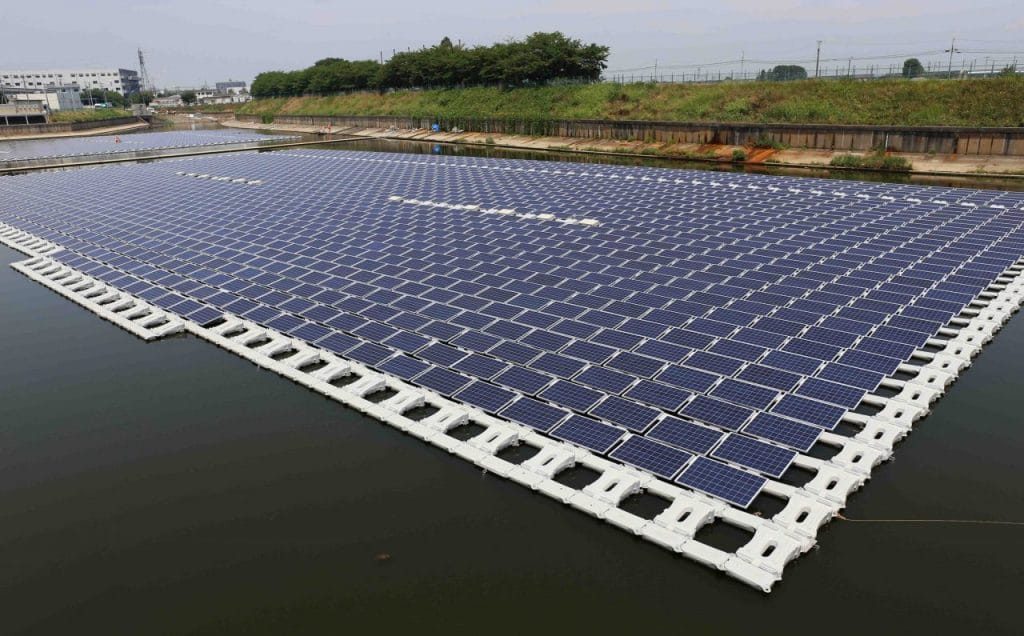
Top 10 floating photovoltaic plants in the world
Every day that passes are more photovoltaic plants that are installed in water all over the world. These floating solar systems or ‘ floatovoltaics ‘ are a suitable solution to situations where the surface on the ceiling or floor is limited. But what is the dimension of this niche market? Where are the existing plants located? What is the size of this energy segment
A work carried out by SolarPlaza at the end of last year quantified in more than 70 the number of floating photovoltaic plants in the world, which just totaled more than 93 MWp. The largest floating plant has a capacity of 40 MWp, while the smallest (5 KW) would fit into the roof of a house. The first floating plant was installed in 2007 in California; A single developer has starred in the construction of more than half of all operating floating plants and 45 of the 70 floating plants are in Japan.
Reduced size
More than half of the existing plants have a capacity of less than 1 MWp. However, this does not mean that floating solar plants can not be large. 21 of the 70 plants are between 1 and 2 MWp, while the remaining 12 are more than 2 MWp. The largest plant has a capacity of 40 MWp and is located in Anhui Province in China. The second largest plant is the solar park Kawashima Taiyou of 7.5 MWp, located in the Saitama Prefecture, in Japan.
Japan, indisputable leader
Many countries have already started experimenting with floating plants. Two countries, however, are the pioneers of a wide margin. The United Kingdom has built 6 floating plants, with capacities ranging from 6.3 MWp to 50 KW, but the current leader in the floating solar market, by far, is Japan, which accomodates 45 of the 70 largest floating photovoltaic plants in the world, and of them 24 are found in the Hyogo Prefecture. Japan’s apparent dominance in this easy-to-explain market segment: generous aid and lack of adequate ground have pushed developers to find creative solutions in the water.
Before 2014, only three floating solar plants had been built in the world. Over the past two years, this number has grown to more than 70 plants spread around the world, which has led many to believe that this is the beginning of a potential new photovoltaic boom. Japan, which has paved the way for the floating revolution, continues to significantly increase the number of its floating plants in operation.
The first of these plants was installed only 3 years ago, in 2013, by West Holdings. By writing these lines there are more than 45 floating plants in Japan, more than half of the existing ones in the world. At the end of last year, at least 29 floating solar plants were báin in charge. Recently Ciel et Terre, a company specializing in floating photovoltaic plants, estimates that another 70 MWp of capacity will be added only in Japan for 2017. This makes it reasonable to think that 2017 could very well become the year of the Floatovoltaics.
Camille Marliere, of Ciel & Terre, one of the largest developers of large-scale floating photovoltaic plants, explains that floating photovoltaic installations are generally located in water ponds, lakes and water reservoirs owned by the Electric companies or agricultural companies. The floating photovoltaic inside is very different from marine floating photovoltaics, which has important limitations for the saltwater environment, wave action and complicated anchorage systems.
Floating solar systems are superior to land or rooftop systems, as they first preserve land for other uses, such as agriculture or livestock. In addition, they reduce water evaporation, covering most of the water surface, also limiting algae growth, and operating more efficiently due to the natural cooling effect of the water.
The only important structural requirements for floating photovoltaic systems are the ability to withstand strong winds, variations in water level and other meteorological challenges.
Today these are the 10 largest floating photovoltaic plants in the world, although since last May the Huainan plant already has 40 MW:
1 Huainan City. 20 MW. China
Anhui China Province is home to the world’s largest floating photovoltaic plant. The plant, 40 MW, is located in a subsidence area of coal mining in the city of Huainan, which currently hosts a fish farm and connected to the network in April 2016, then with a capacity of 20 MW. The plant has completed its second phase of a 300 MW project, as reflected in the agreement signed between Anhui Local government and general contractor Hefei Jntech New Energy. The projected total investment is around $462 million, and will end up occupying an area of more than 1,640 hectares.
The project has been completed by Xinyi Solar, has investors from the also China Sungrow and is expected to contribute to reduce carbon dioxide emissions by more than 420,000 tonnes per year, an objective that has been on the agenda of many regional governments in China for some time.
2 Umenoki. 7.5 MW. Japan
This floating solar plant of 7. 750.4 kWp is installed on a watering raft, located near the city of Higashimatsuyama, Saitama Prefecture, Kanto, Japan.
The Hydrelio floating Solar system supports 27,456 panels (Yingli 275Wp modules), and covers approximately 57.46% of the water surface (7.43 of 12.93 ha).
For this project, Ciel & Terre was responsible for supplying the Hydrelio © system, the design of the Solar Island and the anchorage system. The bottom anchor with ground anchors was designed to meet a maximum depth of 6.9 m and a variation level of 6.9 m. The construction was carried out in 22 weeks and was connected to the network in October 2015.
3 Queen Elisabeth II Reservoir. 6.3 MW. United Kingdom
The solar photovoltaic energy developer Lightsource Renewable Energy has made Europe’s largest floating solar plant at the Queen Elisabeth II Reservoir, located west of London, near Walton-on-Thames. The project consists of 23,000 photovoltaic solar panels and generates sufficient electricity to meet the electrical energy needs of around 1,800 households in the locality.
In the realization of the project Ennoviga Solar used a total of 61,000 floats and 177 anchorages. «This is our largest project outside of Japan and the first with funding from European banking, which demonstrates that our technology is not only suitable for water services, but has also been recognized as being financed in both Europe and Asia.» , said Eva Pauly, director of International Business Development for Ciel et Terre.
4 Otae Reservoir. 3 MW. South Korea
The South Korean developer LG CNS completed the construction of the floating photovoltaic plant in the Otae reservoir in Sangju,-province, in December 2015. The plant was built at the same time as that of the Jipyeong reservoir, and has a capacity of generation of 3 megawatts (MW).
The solar panels cover about 64,000 square meters of water surface – roughly the size of 10 football fields – and generate 8,600 megawatt hours (MWh) per year, enough power to feed 2,400 households. The floating solar plant is also capable of reducing up to 3,600 tonnes of carbon dioxide, almost the same effect as planting 1.2 million of pine, according to the subsidiary of the LG Group.
5 Jipyeong Reservoir. 3 MW. South Korea
The Jipyeong floating photovoltaic plant, as we have just said, was made by LG CNS and connected to the network in December 2015. The plant, as its namesake of Del Embalse Otae has a capacity of 3 MW and is also in the city of Sangju, in the province of-
The solar panels cover about 64,000 square meters of water surface – roughly the size of 10 football fields – and generate 8,600 megawatt hours (MWh) per year, enough power to feed 2,400 households. The floating solar plant is also capable of reducing up to 3,600 tonnes of carbon dioxide, almost the same effect as planting 1.2 million of pine, according to the subsidiary of the LG Group.
6 Godley Reservoir floating Solar PV. 3 MW. United Kingdom
The floating photovoltaic plant of the Godley reservoir was carried out by Forrest for United utilities in Hyde, in Greater Manchester. The plant has a capacity of 3 MW and it has invested 3.5 million is of pounds sterling.
The installation is the largest of the floating photovoltaic system in Europe. The system consists of 12,000 solar panels floating in the reservoir water and covering an area of 45,500 square meters. The installation has 46 steel anchors and has 29,263 primary and secondary floats. United utilities generates in Godley 2.7 GWh annual renewable energy with zero carbon emissions.
7 Kato-Shi. 2.8 MW. Japan
This 2,870.28 kWp floating solar plant is installed in two irrigation rafts, located near the city of Takaoka, in Hyogo Prefecture, Kansai, Japan.
The floating solar System Hydrelio © supports 11,256 panels (Kyocera 255Wp modules), and covers approximately 59.28% of the water surface (3.13 of 5.28 ha).
For this project, Ciel & Terre was responsible for supplying the Hydrelio system, the design of the Solar Island and the anchorage system. The bottom anchor with ground anchors was designed to meet a maximum depth of 5.7 m and a level variation of 5.7 m. The construction of the plant lasted 15 weeks and was connected to the network in March 2015.
8 Tsuga IKE. 2.4 MW. Japan
This 2,449 kWp floating solar plant is installed in a watering tank, located in the city of Susuka, in Mie Prefecture, Japan.
The Hydrelio floating Solar system supports 9,072 panels (270 Wp Kyocera modules), and covers approximately 27% of the water surface (2.48 of 9.21 ha).
For this project, Ciel & Terre was responsible for the supply of the Hydrelio system, the Solar island design and the design of the anchorage system. The bottom anchor with ground anchors was designed to meet a maximum depth of 7.2 m and a variation level of 7.2 m. The construction of the plant was carried out in 8 weeks and was connected to the network in July of 2016.
9 Hara Ike. 2.4 MW. Japan
This 2,397.60 kWp floating solar plant is installed in a water raft, located in the city of Matsusaka, in Mie Prefecture, Chubu, Japan.
The Hydrelio floating Solar system supports 8,880 panels (270 Wp modules from Mitsubishi), and covers approximately 68.89% of the water surface (2.48 of 3.60 ha).
For this project, Ciel & Terre took over the supply of the Hydrelio © system, the design of the Solar Island and the anchorage system. The bottom anchor with ground anchors was designed to meet a maximum depth of 1.8 m and a variation level of 1.8 m. The plant took 20 weeks to build and was connected to the network in March 2016.
10 Sakasama Ike. 2.3 MW. Japan
The Japanese Kyocera Corporation finished building the 2.3-megawatt floating photovoltaic solar power plant on a watering raft in the city of Kasai, in Hyogo Prefecture, west of Japan, in April 2015. The new joint ownership plant of Kyocera and Century Tokyo Leasing Corporation generates 2,680 megawatts (MWh) per year.
The Hydrelio floating Solar system supports 9,072 panels (Kyocera 255Wp modules), and covers approximately 36.66% of the water surface (2.61 of 7.12 ha).
For this project, Ciel & Terre is HIZPO in charge of supplying the Hydrelio system, the design of the Solar Island and the anchorage system. The bottom anchor with ground anchors was designed to meet a maximum depth of 4.5 m and a variation level of 4.5 m. The plant was built in 11 weeks and connected to the network was in May 2015.


















No Comments